| d |
Securities Trading
- Market Order
instructs the floor broker to promptly execute the order at the most
favorable price.
- Limit Order
A buy limit order stipulates that the floor broker executes the order
within the limit set by the customer. If it is a sell limit order, the
broker cannot sell for an amount less than that stipulated. If the price
is touched, it is not guaranteed that the order is executed, since price
moves may be rapid.
- Stop Order
A stop buy order is placed above the current market price and becomes
a market order if the price is touched. A stop sell or stop loss order
is placed below the current market price.
- Open orders: good until cancelled
these orders will continue to be placed for execution until cancelled
by the customer, or filled.
- Stop limit order: stop orders that turn into limit
orders when the stop is exceeded.
Types of Limit Orders
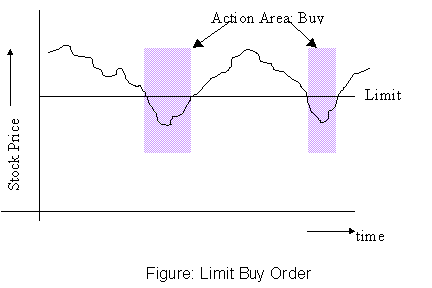
Uses:
- To buy at a specified price or better.
- Used in inactive markets where the possibility of a
stray higher-than-equilibrium price cannot be discounted; hence a market
order is unwarranted.
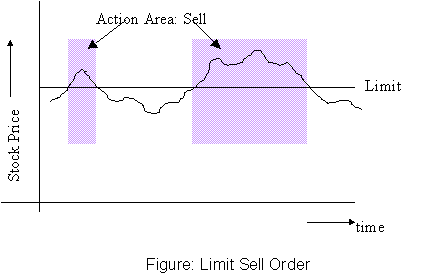
Uses:
- To sell at a specified price or better.
- Used in inactive markets where the possibility of a stray lower-than-equilibrium
price cannot be discounted; hence a market order is unwarranted.
Types of Stop Orders
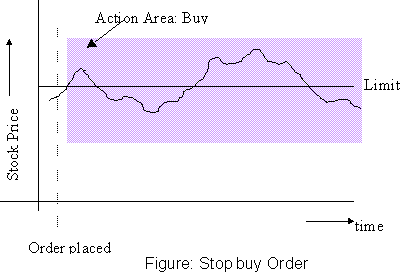
Uses:
- Used in conjunction with a short sale to cut losses where it is feared
that prices might be headed higher.
- Used for protection against an unexpected jump in prices.
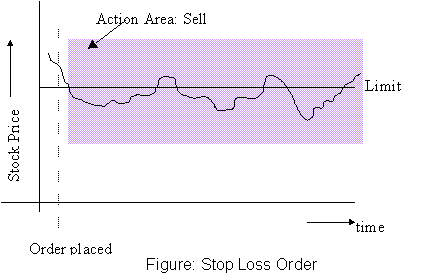
Uses:
- Used to cut losses, by selling existing holdings where it is feared
that prices might be headed lower.
- Used for protection against an unexpected slide in prices.

Trading
When trading on a quote-driven exchange, a trader needs to keep in mind
several things:
- The Bid quote is the price at which the trader is required to buy
the minimum number of shares
- The Offer quote is the price at which the trader is required to sell
the minimum number of shares.
- The bid quote is (almost) always is lower than the offer quote.
- The difference between the offer (ask) quote and the bid quote is
called the bid-ask spread.
- If the bid quote is higher than the ask quote, then we say that the
market is crossed.
- If the trader has too high an inventory of the stock, he may not want
his Bid quote to be the inside bid.
- If the trader has committed to too many sales (short-sold), he may
not want his Offer quote to be the inside offer.
- If the market is expecting news, the trader may want either his Bid
or his Offer to be the inside quote if he is himself not informed; else,
he may be forced to make undesirable trades.
- Watch price trends, so that the trader is not caught with an unexpected
inside quote.
|
|